Column: The Trouble with Gas
In 2011, the David Suzuki Foundation and the Pembina Institute released a report analyzing whether “natural” gas could be considered a “bridging fuel” during the necessary transition from fossil fuels to renewable energy. It concluded that Canada should focus on developing more renewable energy, not fossil fuels, including gas. Yet, after many years, as prices for renewable energy drop and technologies continue to improve, some are still touting fossil gas as a “bridge fuel” — or even a climate solution.
A couple of new reports, including one prepared for the David Suzuki Foundation, show that fossil gas is actually a costly bridge to more pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
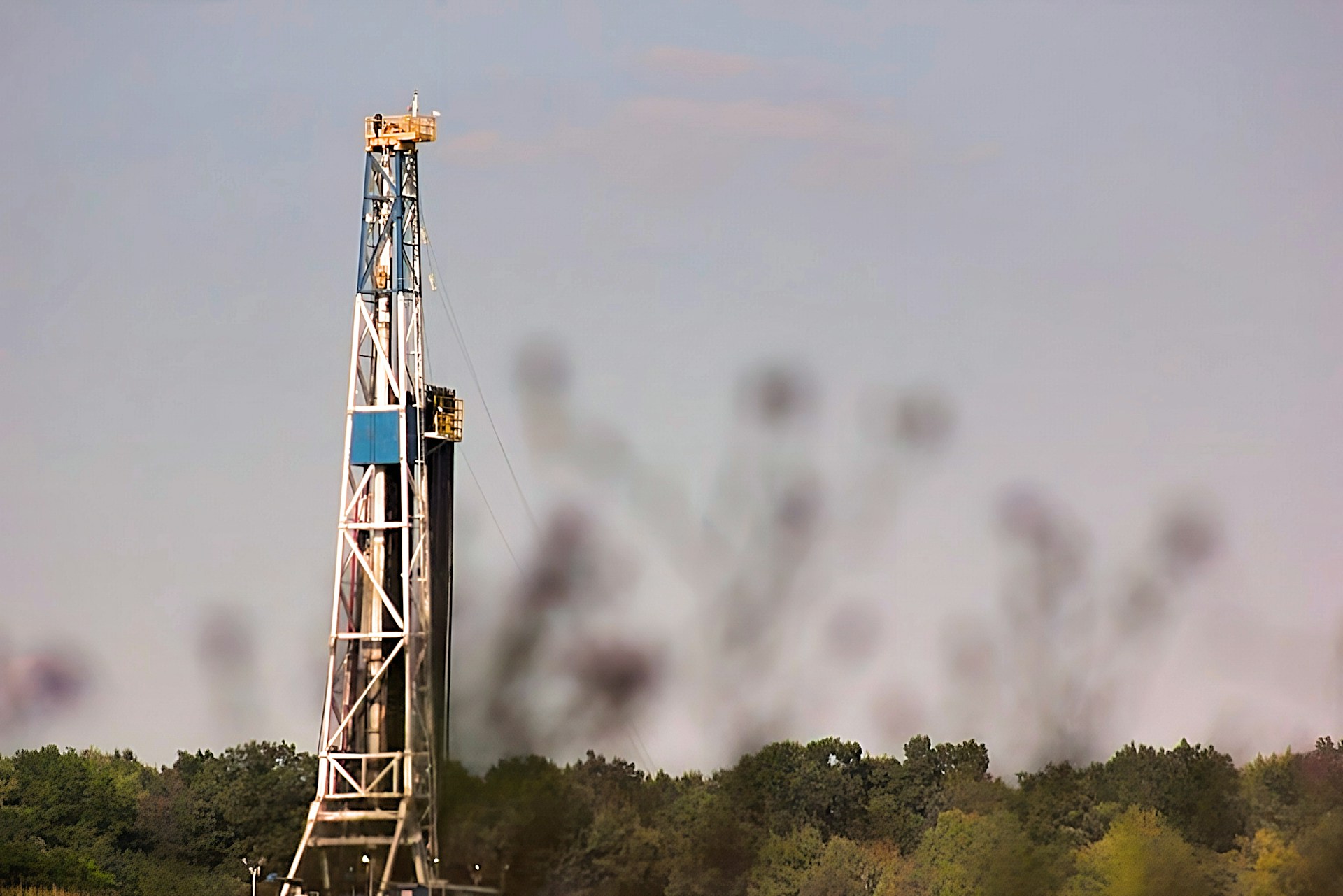
Since 2011, we’ve learned more about fossil gas problems, especially considering that most is now obtained from “unconventional” reserves. That means hydraulic fracturing, or fracking, for shale gas, in which difficult-to-extract gas is released and brought to the surface by pumping massive amounts of pressurized liquids and chemicals into the ground to break up rock and rock formations. It’s a relatively expensive process and uses enormous amounts of water.
One new report finds not only that fossil gas isn’t an adequate “bridge fuel” but that exported gas also has a greater climate impact than coal over a 20-year period. Production and liquefying shale gas to make liquefied natural gas, or LNG, uses a lot of energy. The gas is mostly methane, which is a more potent greenhouse gas than carbon dioxide over the short term. Leaks, deliberate venting and incomplete combustion during extraction, production and transport can cause significant climate impacts. Studies, including some by the David Suzuki Foundation, have found that methane leaks are far higher than industry and governments estimate.
The Cornell University report, published in Energy Science & Engineering, found that burning the gas accounts for 34 per cent of its greenhouse gas footprint, while “upstream and midstream” methane emissions make up 38 per cent. Including the energy required to produce LNG brings it to 47 per cent. The liquefaction process and tanker transport add to the total. The global warming potential of LNG as a fuel is 33 per cent greater than that of coal over a 20-year period (and is still equal to or greater than coal over a 100-year period), the report concludes.
“To think we should be shipping around this gas as a climate solution is just plain wrong,” report author Robert Howarth, an environmental scientist, told the Guardian. “It’s greenwashing from oil and gas companies that has severely underestimated the emissions from this type of energy.”
Focusing on timelines through the lens of election cycles, unimaginative politicians often see gas production as a quick and easy economic boost, and so they buy into industry propaganda and greenwashing. That’s led to support and subsidies to propel a possible LNG-for-export boom in British Columbia.
A new report from Carbon Tracker with the David Suzuki Foundation and the Pembina Institute shows that’s not a viable solution. “Turning Tides: The economic risks of B.C.’s LNG expansion in a changing energy market” finds that continuing and expanding B.C.’s LNG-for-export industry is a risky investment. The International Energy Agency reports that LNG export capacity will exceed demand, which will “depress international gas prices and set the stage for fierce competition between suppliers.”
Whether the transition is fast or slow, returns will be minimal. As for global markets, large volumes can be supplied at lower prices from producers including Qatar, Australia and Mozambique. Asian markets are uncertain and appear to be contracting. That means the four LNG terminals in B.C. waiting for investment decisions will likely not be able to compete with lower-cost suppliers on global markets.
No matter how hard the fossil fuel industry and its supporters try to keep their destructive, outdated industry alive, it’s time to face reality. Fracking for more climate-altering gas is not a solution, for the climate or economy. We have cheaper, cleaner and healthier ways to produce energy. We also need to redouble efforts to improve energy efficiency, doing more with less and saving money in the process. There’s no room for more fossil fuel development — whether it’s coal, oil or gas — on a rapidly overheating planet.
It’s time to leave all fossil fuels in the ground — including gas!
David Suzuki is a scientist, broadcaster, author and co-founder of the David Suzuki Foundation. Written with David Suzuki Foundation Senior Writer and Editor Ian Hanington.
Learn more at davidsuzuki.org.


























Comments